Product number:
103112SO24
Product information "Alfa Rpar - AS3052D - NPN Transistor Array"
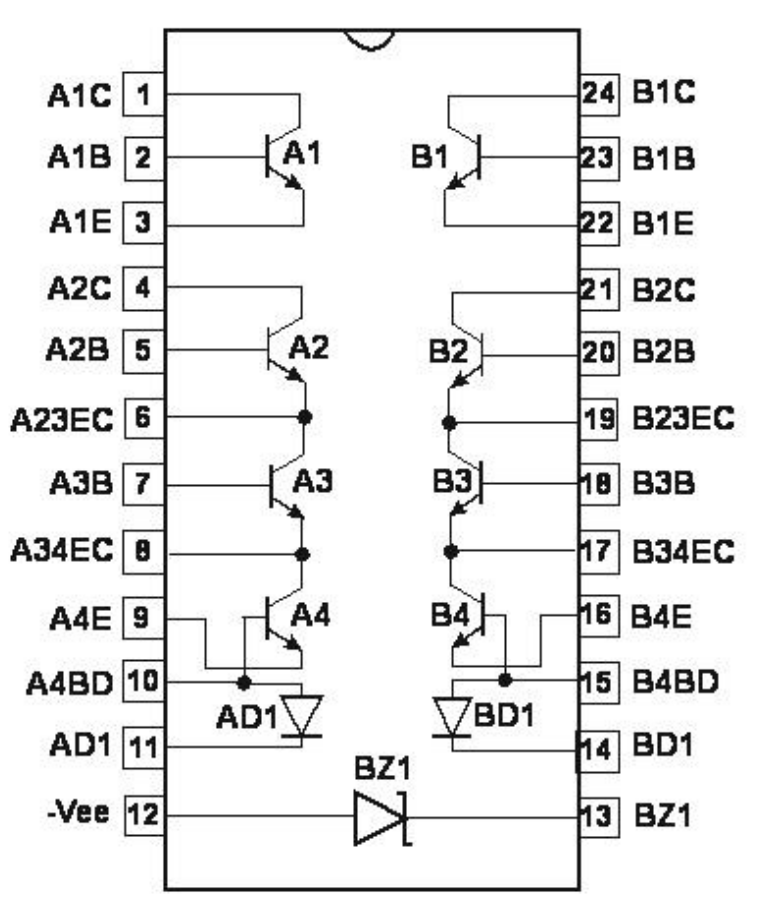
The AS3052 consists of 8 NPN transistors, 2 diodes and 1 buried zener on a common monolithic substrate. Transistor array allows variety of connections - differential pairs, different type of current sources, and different kind of multipliers/dividers. They may be used as discrete transistors in conventional circuits, however in addition, they provide the very significant inherent integrated circuit advantages of close electrical and thermal matching.
Features:
• 8 matched npn transistors, 2 diodes, 1 burried zener diode
• VBE matched less than ±1 mV
• wide operating current range
Applications:
• filters (Moog type)
• multipliers (like MC1496)
• dividers
• Gilbert cells
• custom designed differential amplifiers
• temperature compensated amplifiers
Features:
• 8 matched npn transistors, 2 diodes, 1 burried zener diode
• VBE matched less than ±1 mV
• wide operating current range
Applications:
• filters (Moog type)
• multipliers (like MC1496)
• dividers
• Gilbert cells
• custom designed differential amplifiers
• temperature compensated amplifiers
| Basic Function: | NPN Transistor Array |
|---|---|
| IC Package: | SOIC-24 (SMT) |
| Pin Count: | 24 |
| Pin Pitch [mm]: | 1,27 |
| Technology: | SMT |
Manufacturer / Hersteller:
ALFA RPAR AS
Ropažu iela 140
Vidzemes priekšpilsēta
LV-1006 Rīga
Lettland
alfa@alfarzpp.lv
Safety Instructions for Electronic and Mechanical Components
Intended Use:
• Electronic components, including potentiometers, knobs, switches, connectors, resistors, capacitors or integrated circuits (ICs), are designed for use in electronic circuits and devices.
• Use these components only for their intended purposes in electrical and electronic applications, according to their specified voltage, current, and environmental conditions.
• Any use outside the intended applications may result in malfunction or safety risks.
Handling and Installation
Installation:
• Handle electronic components with appropriate tools, such as tweezers, to avoid physical damage or exposure to electric shock.
• Ensure that the components are installed in the correct orientation and according to manufacturer specifications to avoid malfunction or damage to the circuit.
Storage:
• Store components in a dry, cool, and static-free environment to avoid damage from moisture, extreme temperatures, or electrostatic discharge (ESD).
• Avoid direct exposure to sunlight, which could affect component stability and performance.
Protection from Static Electricity:
• Use antistatic equipment (e.g., wrist straps, ESD mats) when handling electronic components to prevent electrostatic discharge, which can damage sensitive devices like ICs.
Compatibility:
• Make sure electronic components are compatible with the circuit in terms of voltage, current, and other technical specifications.
Warnings
Electrical Shock Hazard:
• Some components can retain charge even when disconnected. Use appropriate tools and take precautions when handling components to minimize the risk of electric shock.
Burn or Fire Risk:
• Overloading or misusing electronic components may result in overheating, which could lead to burning or fires. Ensure that components are used within their specified voltage and current ratings.
Danger from Misuse:
• Incorrect handling or use outside specified limits can damage the components or affect the performance and functionality of connected devices. Only use components within their specified tolerances and conditions.
Choking Hazard:
• Small electronic components can pose a choking hazard if swallowed. Keep components out of reach of children.
ALFA RPAR AS
Ropažu iela 140
Vidzemes priekšpilsēta
LV-1006 Rīga
Lettland
alfa@alfarzpp.lv
Safety Instructions for Electronic and Mechanical Components
Intended Use:
• Electronic components, including potentiometers, knobs, switches, connectors, resistors, capacitors or integrated circuits (ICs), are designed for use in electronic circuits and devices.
• Use these components only for their intended purposes in electrical and electronic applications, according to their specified voltage, current, and environmental conditions.
• Any use outside the intended applications may result in malfunction or safety risks.
Handling and Installation
Installation:
• Handle electronic components with appropriate tools, such as tweezers, to avoid physical damage or exposure to electric shock.
• Ensure that the components are installed in the correct orientation and according to manufacturer specifications to avoid malfunction or damage to the circuit.
Storage:
• Store components in a dry, cool, and static-free environment to avoid damage from moisture, extreme temperatures, or electrostatic discharge (ESD).
• Avoid direct exposure to sunlight, which could affect component stability and performance.
Protection from Static Electricity:
• Use antistatic equipment (e.g., wrist straps, ESD mats) when handling electronic components to prevent electrostatic discharge, which can damage sensitive devices like ICs.
Compatibility:
• Make sure electronic components are compatible with the circuit in terms of voltage, current, and other technical specifications.
Warnings
Electrical Shock Hazard:
• Some components can retain charge even when disconnected. Use appropriate tools and take precautions when handling components to minimize the risk of electric shock.
Burn or Fire Risk:
• Overloading or misusing electronic components may result in overheating, which could lead to burning or fires. Ensure that components are used within their specified voltage and current ratings.
Danger from Misuse:
• Incorrect handling or use outside specified limits can damage the components or affect the performance and functionality of connected devices. Only use components within their specified tolerances and conditions.
Choking Hazard:
• Small electronic components can pose a choking hazard if swallowed. Keep components out of reach of children.
Login